 |
Non-radioisotope complete kit useful for the screening of anti-diabetic drugs as well as in the research area of glucose metabolism and insulin signaling.
2-Deoxyglucose (2DG) Uptake Measurement kit
Background
Measurement of 2-deoxyglucose (2DG) uptake in tissues and cells is a reliable approach with which to estimate glucose uptake and thereby to explore the regulation of glucose metabolism and mechanism of insulin resistance. Radioisotope-labeled 2DG is usually used for the measurement of 2DG uptake both in vivo and in vitro. However the radioisotope (RI) method is required a specialized facility for RI in strict limitation and cannot be handled in ordinal laboratories. Furthermore, radioactive 2DG administered into cultured cells remains in the extracellular space, and therefore the results must be corrected by separating the extracellular 2DG and intracellular 2DG/2DG-6-phosphate (2DG6P) in the cells.
This kit is based on the enzymatic method for the direct measurement of 2DG6P amount without any use of radioisotope materials (Saito K and Minokoshi Y, et al. Analytical Biochem 412: 9-17, 2011).

Small amount of 2DG is administered into animals or cultured cells, and endogenous glucose and glucose-6phosphate (G6P) in tissues or cells is oxidized in the presence of a low concentration of G6PDH. 2DG-6-phosphate (2DG6P) accumulated in cells is then oxidized in the presence of a high concentration of G6PDH. NADPH produced from 2DG6P and G6PDH is quantified at 420 nm with the use of a recycling amplification enzymatic-photometric system. The novel enzymatic method can quantify 2DG or 2DG6P in the range of 5-80 pmol. As all enzyme reactions were performed in one 96-well microplate by the sequential addition of reagents, this method can be adopted for an industrial robot. This method is useful for the screening of anti-diabetic drugs as well as in the research area of glucose metabolism and insulin signaling.
Principle
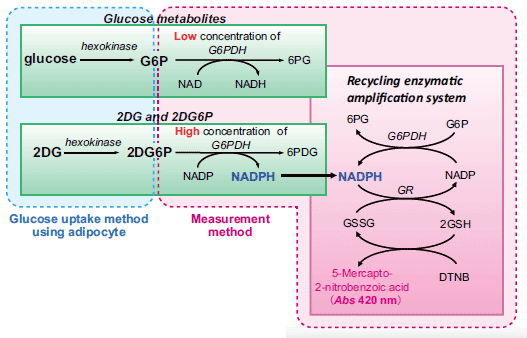
1) Oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) with a low concentration of G6P dehydrogenase (G6PDH) plus NAD+ to eliminate endogenous G6P in target cells.
2) Elimination of NAD(P)H with HCl, which removes endogenous NAD(P)H as well as NADH produced in step 1.
3) Production of NADPH through oxidation of 2DG6P in the cells with a high concentration of G6PDH, with the NADPH being used for quantification of 2DG6P.
4) Elimination of NAD(P)+ and G6PDH remains after step 2 with NaOH.
5) Recycling amplification reaction for the small amount of NADPH produced, and quantification of 2DG6P with a (96-well microplate) photometric reader.
DBA-ITALIA Srl
Via Umbria 10
20090 Segrate (Milano)
Tel. +39 02-26922300
Fax +39 02-26926058
Fax +39 02-26923535