|
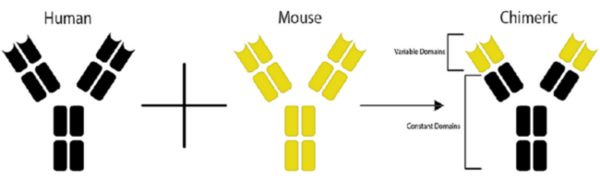
Chimeric
antibodies are antibodies
made up of gene fragments from different species. Combined through a
genetic engineering process, these gene fragments form a novel molecule
with unique properties.
Chimeric
antibodies were developed due to poor effectiveness of mouse antibodies
in human therapeutics owing to the immune response triggered by the
presence of foreign mouse proteins. Chimeric antibodies provide a
solution to this problem by maintaining constant regions of a human
antibody, linked to variable regions of mouse
antibody. This combination of the two species’ antibody regions reduces
immunogenicity whilst still allowing for high binding specificity.
|
.png)